Asset vs Non-Asset Intermodal Freight Providers: A Detailed Comparison
October 22, 2024 •Rick LaGore

As we engage with shippers across North America on the merits of intermodal shipping, one common sentiment we hear is: “We only work with asset intermodal providers.”
This viewpoint is easily understandable in the truckload world, where motor carriers own all the assets needed to transport goods from origin to destination. In contrast, an intermodal freight move involves a variety of assets: trains, locomotives, well cars, rail tracks, intermodal ramps, train crews, freight tractors, chassis, and truck drivers.
As we break down the asset components further in this article, you'll see that no single intermodal service provider owns 100% of these assets. This highlights the complexity of defining an "asset" intermodal provider, especially when compared to asset-based truckload carriers.
Because the concept of "asset ownership" is more nuanced in the 53' intermodal transportation market, many shippers miss out on substantial capacity and cost-saving opportunities. This article will clarify what "asset" and "non-asset" mean in the intermodal transportation space.
The 53' Intermodal Market
The 53' intermodal market comprises several types of intermodal providers: bi-modal, asset-lite, non-asset, rail retailers, and freight brokers. In other words, intermodal services cannot be divided simply into asset and non-asset providers, as they often are in the truckload market.
That said, we want to emphasize that a true intermodal service provider, also known as an intermodal marketing company (IMC), is not "just another broker." Instead, IMCs act as advocates for Class I railroads, utilizing their assets to add value to a company's logistics and supply chain strategies.
Definition of an IMC
An Intermodal Marketing Company (IMC) purchases rail and truck transportation services, uses equipment from multiple sources, and provides value-added services under a single intermodal freight bill. This comprehensive service model simplifies the shipper’s experience.
IMCs arose as railroads, during the development of intermodal services, decided not to sell directly to shippers. Instead, they chose to sell wholesale to IMCs, which would handle sales, marketing, and operational tasks.
IMCs have since evolved to handle:
- Operational work: Securing containers, arranging drayage, and tracking shipments through delivery.
- Customer service: Offering support and reporting that shippers expect.
- Geographic reach: Providing access to both West and East Coast intermodal combinations, something no single railroad can achieve on its own.
Types of Asset and Non-Asset IMCs
IMCs are classified into several categories, each with distinct characteristics:
Bi-Modal IMCs
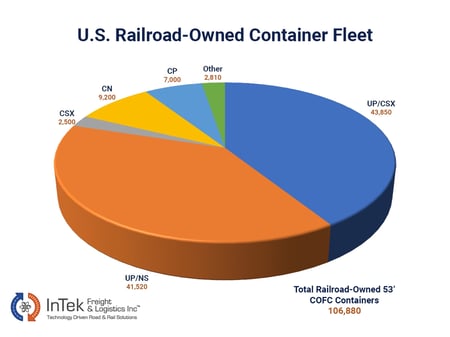
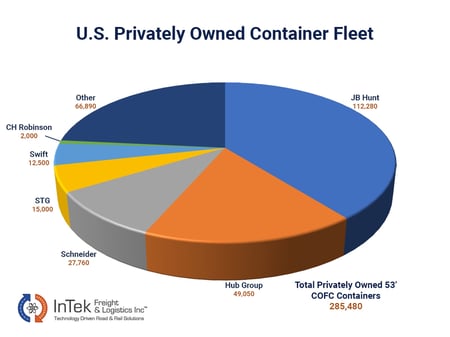
These providers own containers, chassis, and the majority of their drayage capacity (tractors and drivers). However, they do not own trains, tracks, intermodal ramps, or employ railroad personnel. A well-known example of a bi-modal IMC is JB Hunt.
Asset-Lite IMCs
Asset-lite IMCs, like Schneider, own containers and drayage assets but do have a portion of their business where they will augment customer capacity with railroad-owned equipment when demand exceeds their capacity.
Non-Asset IMCs
Non-asset IMCs, such as InTek Freight & Logistics, do not own containers or drayage assets. Instead, they leverage railroad-owned equipment and private box owners. In some cases, non-asset IMCs may utilize ocean carriers' empty 40' containers for domestic shipping, creating cost-saving opportunities.
Rail Retailers
This small segment comprises railroads selling directly to shippers. Canadian National (CN) and Canadian Pacific (CP) are the only two companies in this category. While their service is solid, some shippers find the direct railroad model lacks the customer service and operational support of an IMC.
Freight Brokers
Freight brokers use services from all intermodal provider segments but do not have direct relationships with railroads. They rely on IMCs or bi-modals to deliver intermodal services to their customers. Many, not all, freight brokers do not know all the nuances of intermodal, so would caution utilizing a freight broker for intermodal services unless they have some type of agency agreement where they are tied in closely on intermodal service.
Comparing Asset & Non-Asset Intermodal Service Providers
The choice between asset and non-asset IMCs depends on a shipper’s specific needs. Each model offers distinct advantages:
Advantages of Bi-Modals
- Synergies: Bi-modals, such as JB Hunt, can leverage their internal resources, providing unique synergies for specific lanes.
- Economies of scale: They often use one West Coast and one East Coast railroad for cost efficiency.
- Truckload balance: Bi-modals may balance truckload capacity to offer unconventional intermodal lanes.
However, bi-modals are limited to their own assets and the railroads they partner with, which can restrict the range of origin and destination combinations they can service.
Advantages of Asset-Lite and Non-Asset IMCs
- Flexibility: Asset-lite IMCs offer greater flexibility by tapping into both their own and railroad-owned equipment.
- Wide reach: Non-asset IMCs have the advantage of access to all Class I railroads, offering shippers the ability to diversify their supply chain and reduce risk.
- Expanded capacity: Non-asset IMCs can also access additional capacity from ocean containers, offering cost-effective solutions.
Non-asset IMCs offer comprehensive coverage across all Class I railroads, providing flexibility and a one-stop-shop experience for shippers.

Asset or Non-Asset: How to Decide
When selecting an IMC, shippers should consider:
- Asset Ownership: While asset IMCs tout reliability through ownership, non-asset IMCs often have more access to a wider range of containers and intermodal service providers.
- Service & Process Ownership: Both asset and non-asset IMCs offer high levels of service, but non-asset IMCs working with Class I railroads’ door-to-door service can also provide superior reliability.
- Rail Relationships: Direct relationships with railroads are crucial. Both asset and non-asset IMCs typically have these relationships, ensuring reliable rail services.
- Financial Commitment: Asset IMCs claim that owning assets proves their commitment, while non-asset IMCs invest heavily in the back office processes and their deep and wide relationships with railroads and dray companies used in their intermodal solution to exceed their customers' needs. This is not to say that asset IMCs do not invest heavily in technology because they most certainly do.
- Experience: Experience in the intermodal market varies widely among IMCs, so shippers should carefully evaluate their options. They should also evaluate the customer service - dispatch operations of both to understand how their business will be serviced because that touchpoint is often the linchpin in the success of the intermodal service received.
Summary
In conclusion, the critical differentiator in intermodal services is not asset ownership but the ability to provide high-quality service. With only nine North American railroads, every IMC, asset or non-asset, uses the same rail network. The true deciding factors are the service level, drayage management, and communication processes.
As you search for the best IMC for your business, remember that both asset and non-asset providers have unique strengths. Larger shippers often diversify between both models, while smaller to mid-sized companies may prefer the simplicity of a non-asset IMC for all their intermodal needs.
The good news is shippers have several great asset and non-asset IMC options to choose from as they implement their intermodal strategy. The solution can be the best of breed solution, or they can go with a single type of intermodal solution.
There are exceptions to every rule, but what we tend to find is the bigger shippers go with a best of breed solution of asset truckload intermodal diversifying across both asset and non-asset IMCs, while the smaller to medium size companies choose the non-asset IMC’s for simplicity of being able to call one provider for all their intermodal needs.
Whether you're looking to transition lanes over 700 miles into a cost-saving, capacity-rich intermodal solution, or simply seeking advice, InTek is here to help.
As you work through your search on the best IMC for your business, please don’t hesitate to reach out to InTek. We’ve been able to help hundreds of shippers in adding additional intermodal capacity or transition over truckload lanes to intermodal for both cost and capacity benefits.
Below are the top 5 most popular articles that have been read by our customers today to get them into the intermodal market successfully.
-
The Complete Guide to Intermodal Transportation
-
Intermodal Marketing Company (IMC) - Definition, Purpose & Value)
-
JB Hunt's Intermodal Model vs Class I Railroads: Pros and Cons of Each
-
Intermodal Options Beyond JB Hunt, Hub Group, Schneider, STG & Swift
-
11 Differences Between Intermodal and Truckload Every Shipper Should Know
If you're ready to take the next step, at InTek Freight & Logistics, we can help. Just tell us what you need and we'll discuss how our expertise can help with the unique shipping challenges your business faces. Rather do a bit more research first? View our Freight Guides for comprehensive articles and eBooks on all things freight and logistics.
Get Updates
Featured Articles
Categories
- Freight & Shipping Costs (54)
- Freight Broker (62)
- Freight Forwarder (2)
- Intermodal Transportation (186)
- International & Cross Border Logistics (43)
- Logistics & Supply Chain (422)
- Logistics Service Provider (77)
- LTL (39)
- Managed TMS (49)
- News (39)
- Supply Chain Sustainability (12)
- Transportation Management System (37)
- Truckload (122)
- Warehousing & Distribution (50)